
In a world first, NASA’s DART mission is about to smash into an asteroid. What will we learn?
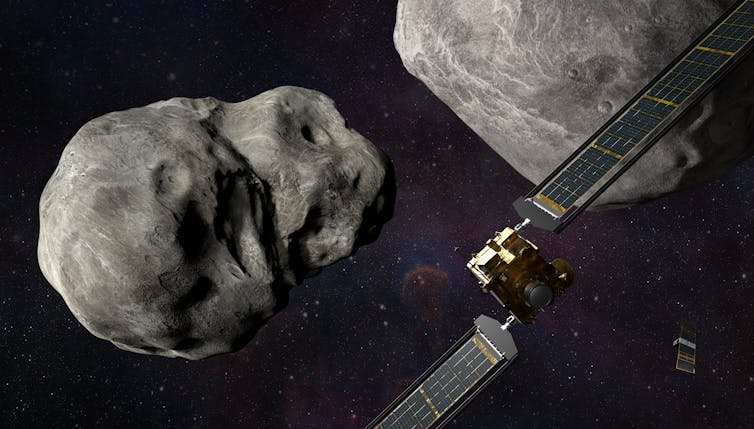

Illustration of DART prior to impact.
NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben
On September 26 at 11.15pm UTC, NASA’s DART mission (Double Asteroid Redirection Exam) will be the 1st to intentionally and measurably change the motion of a considerable body in our Solar Technique. In other phrases, it will smash into an asteroid.
The mission will give the first examination of a method that could be employed in the upcoming – to redirect any asteroids we detect on a collision class with Earth.
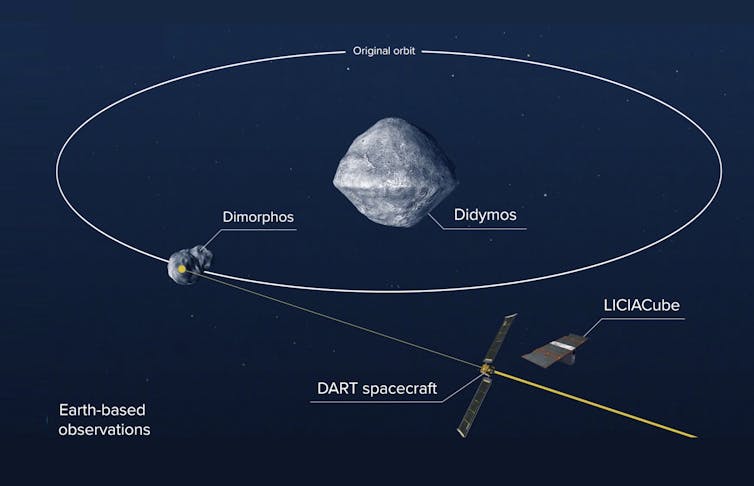
A binary pair of area rocks
DART was introduced on November 24, 2021, its desired destination a pair of asteroids in orbit all over each other, 11 million kilometres from Earth.
The much larger asteroid in the pair is named Didymos and is 780 metres in diameter. The more compact asteroid, just 160 metres large, is named Dimorphos. The two orbit every single other at a distance of 1.18 kilometres, and one orbit can take shut to 12 hrs.
NASA/Johns Hopkins APL
These asteroids pose no risk to Earth and have been decided on as the target for DART partly owing to that point. But also, importantly, since the asteroids form a binary pair, it will be attainable for astronomers on Earth to assess the final results of the impact.
As the asteroids orbit each other, the sunlight reflected off them will increase and decreases, various systematically in excess of the 12-hour cycle of the orbit. Astronomers employing highly effective telescopes from Earth can check this variation and see how it variations, from ahead of to right after the collision.
![]()
The physics is basic, the mission is not
The physics seems very simple, and it is. Strike one detail with an additional point to improve its movement. But the mission execution is really challenging. When DART reaches the asteroids, it will be 11 million kilometres from Earth following a 10 month journey. The spacecraft has to use autonomous concentrating on, making use of images of the asteroids it acquires as it methods.
DART needs to recognise the asteroids by itself, quickly lock onto Dimorphos, and alter its trajectory to strike it. This is all while going at a pace of just about 24,000 kilometres for every hour!
The effects of the impression, though reasonably simple to evaluate, are tricky to predict. The dimensions, form, and composition of Dimorphos, and specifically the place DART hits and how challenging, will have an effect on the outcome.
All these factors are unsure to some degree. Detailed computer system simulations of the effect have been carried out, and the comparisons of the simulations, predictions, and measured final results will be the main results of the DART mission.
As properly as the measurements from telescopes on Earth, an up-close check out of the affect alone will be possible, from an Italian Area Agency CubeSat (a little form of satellite) termed LICIACube that was deployed from a spring-loaded box aboard the craft on 11 September. LICIACube will stick to alongside and photograph the collision and its aftermath.

Lowell Observatory
The benefits will explain to us a ton about the nature of asteroids and our skill to modify their motions. In the long run, this information could be employed to approach planetary defence missions that search for to redirect asteroids deemed to be a risk to the Earth.
What is the amount of menace?
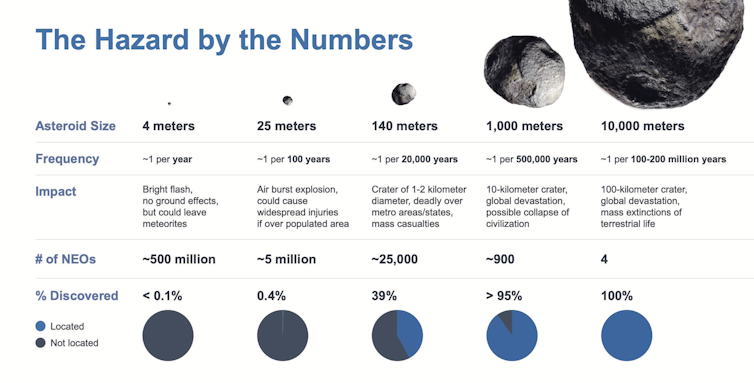
An asteroid as little as 25 metres in diameter could make injuries from an airburst explosion if it hit the environment around a populated region. It is believed that 5 million this sort of objects exist in our Photo voltaic Technique and that we have found somewhere around .4% of them. These a hit is approximated to happen once each and every 100 many years. Even though rather regular, the total threat is very low and the affect chance is reasonably reduced also.
However, it is predicted there are 25,000 objects in the Photo voltaic Procedure the measurement of Dimorphos, 39% of which are recognized, that hit Earth each 20,000 a long time. These kinds of an item would lead to mass casualties if it strike a populated spot.
NASA
Asteroids that could obstacle the existence of human civilisation are in the 1 km furthermore measurement category, of which there are fewer than a thousand in the Photo voltaic Technique they may possibly hit Earth only just about every 500,000 decades. We have presently located 95% of these objects.
So, possible asteroid collisions with Earth array from the regular but benign to the pretty unusual but catastrophic. The DART checks are staying carried out in a quite related and fascinating dimensions assortment for asteroids: these greater than 100 metres.
If DART is effective, it might established the scene for upcoming missions that goal asteroids, to nudge them out of the way of collisions with Earth. When an asteroid is a long way from Earth, only a tiny nudge is necessary to get it out of our way, so the before we can detect asteroids that are a possible danger, the superior.
In the near long term, the perfectly-worn premise of so numerous “an asteroid is coming, we need to have to deflect it!” videos might properly develop into a fact.
Steven Tingay, John Curtin Distinguished Professor (Radio Astronomy), Curtin University
This posting is republished from The Dialogue underneath a Inventive Commons license. Browse the primary write-up.
